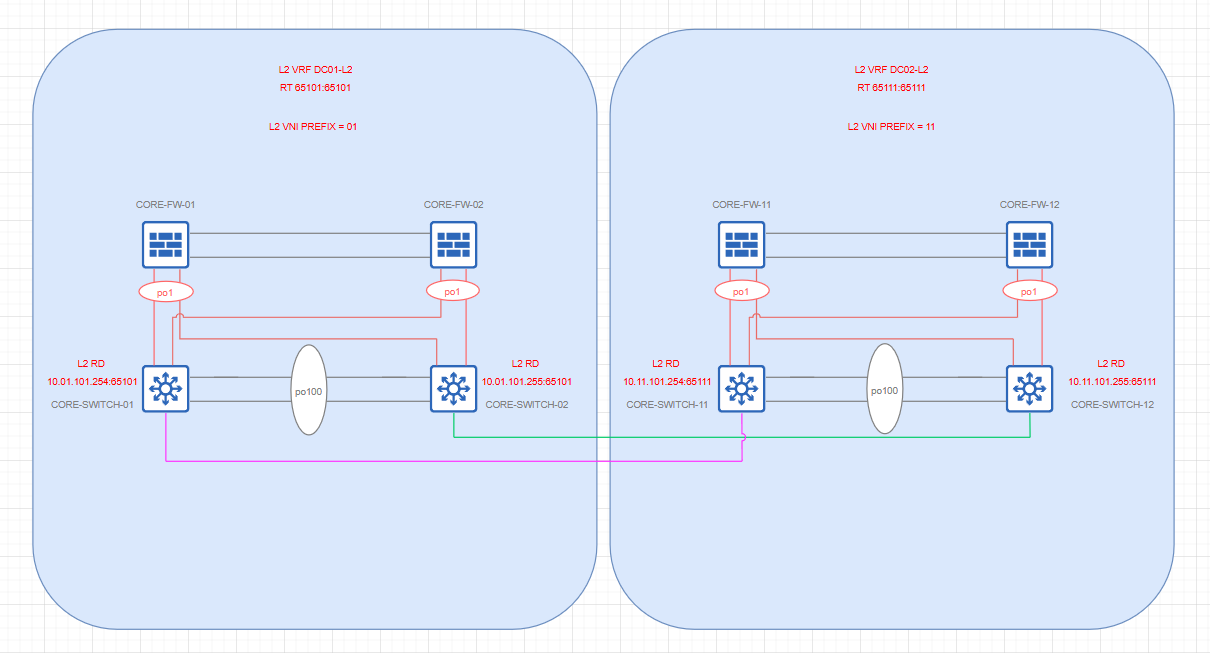
EVPN – Local VRF
As mentioned earlier, EVPN was adopted to allow network segmentation at Datalink and Network layers along with network extension (L2/L3 VPNs) where relevant
The “Local” VRF represents a Layer 2 domain isolated to a datacenter making sure the traffic is not traversing the backhaul.
Each EVPN VTEP represented by a single core switch configured with a route distinguisher and a route target map, thus allowing EVPN peers to learn and maintain only respective routes.
In example (refer to the diagram below) RD for DC01 VTEPs is IP:65101 with DC11 VTEPs having RD of IP:65111. This is basically a “tagged” representation of the L2 routes originated from the VTEP.
Then we have route targets defined for import/export as 65101:65101 for DC01 and 65111:65111 for DC11 to isolate certain “tagged” routes to the respective Datacenter
L2 VNI prefix for DC01 VLAN to VNI mappings has been chosen as 01, with 11 reserved for DC11.